Data Table UX: 5 Rules of Thumb
3 minute read | Dec 27, 2022
product
Here are five rules of thumb to follow when designing user friendly data tables for a web app:
- First column readable
- Default sort by most common query
- Place filters close to headers
- View more fields using quick view
- Use pagination for more records
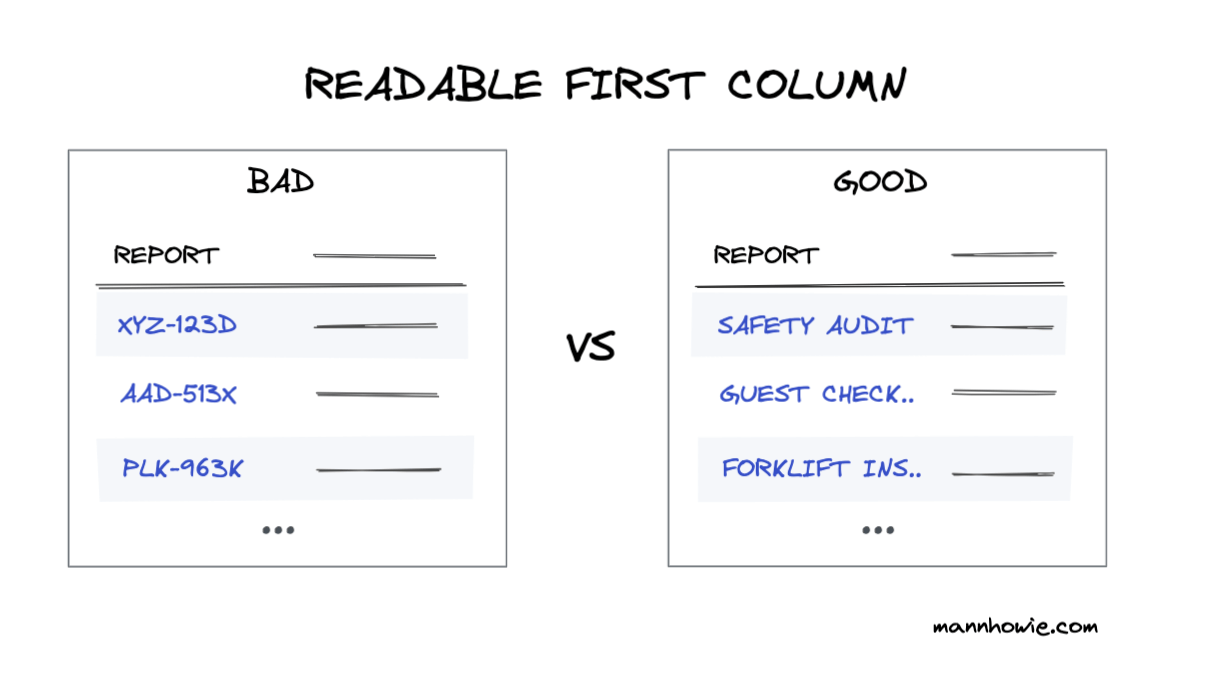
1. First column readable
Use human readable text for the first column. Do not use ids meant for record keeping. It should easily convey meaning about the record. It's ok if you have duplicate names.
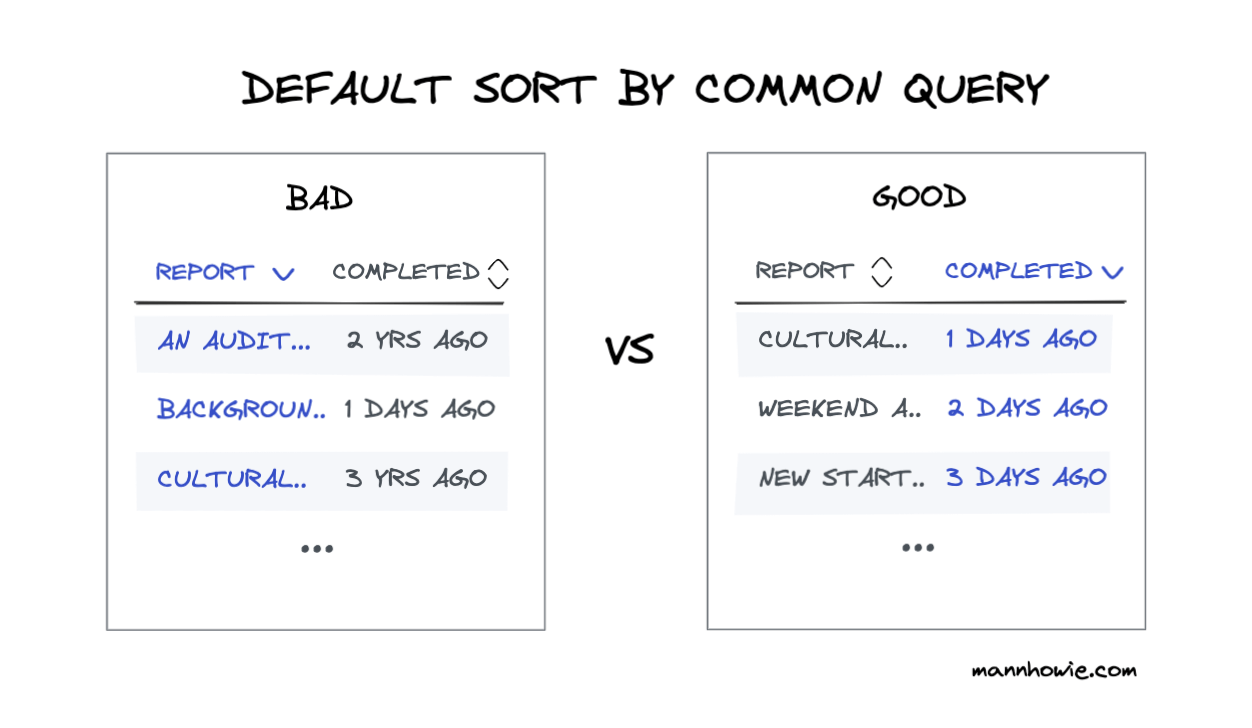
2. Default sort by most common query
Decide what most users should first query when using your data table. Make this your default sort order when navigating to the table. Avoid sorting alphabetically by the first column.
Bonus: Develop your data table to support dynamic urls for custom sort and filter options. Use this to design email campaigns for different tasks (e.g. follow up on overdue items, update your assigned items, shout out recently completed items).
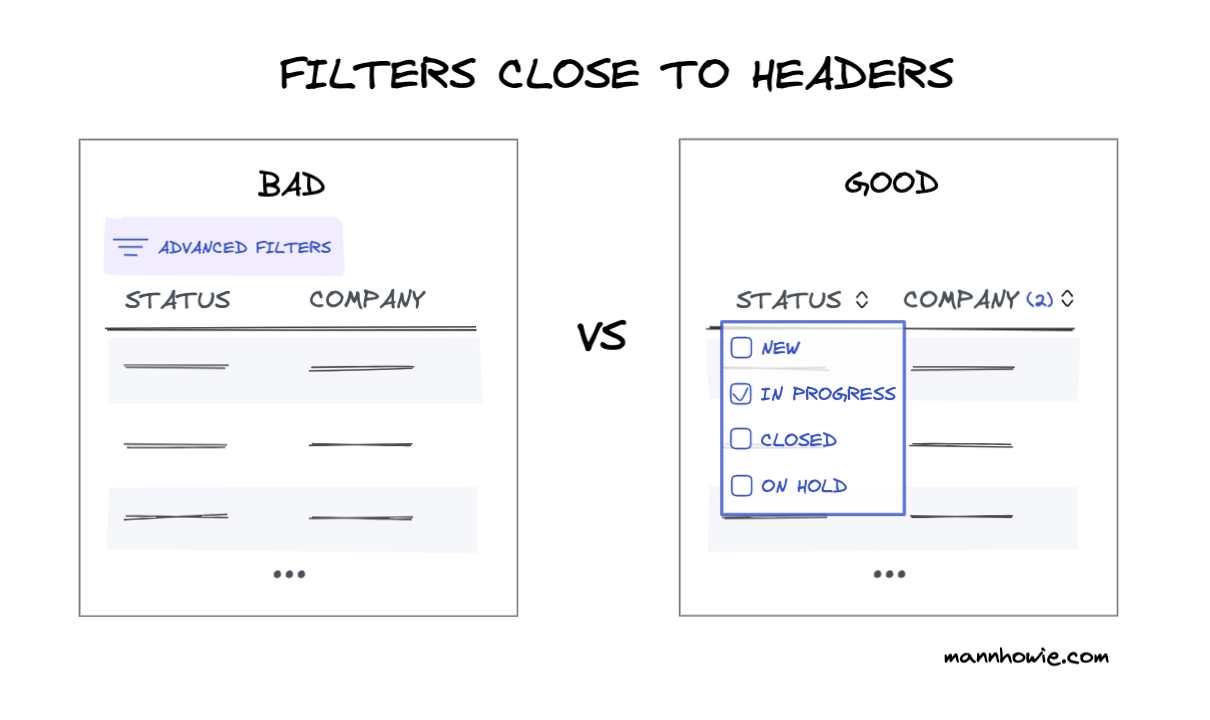
3. Place filters close to headers
Filters with good mapping should be placed close to the columns and headers that they control. Take advantage of spreadsheet conventions where column headers control sorting and filtering. Avoid advanced filter options placed outside your data table which can be hard to find and interrupt flow.
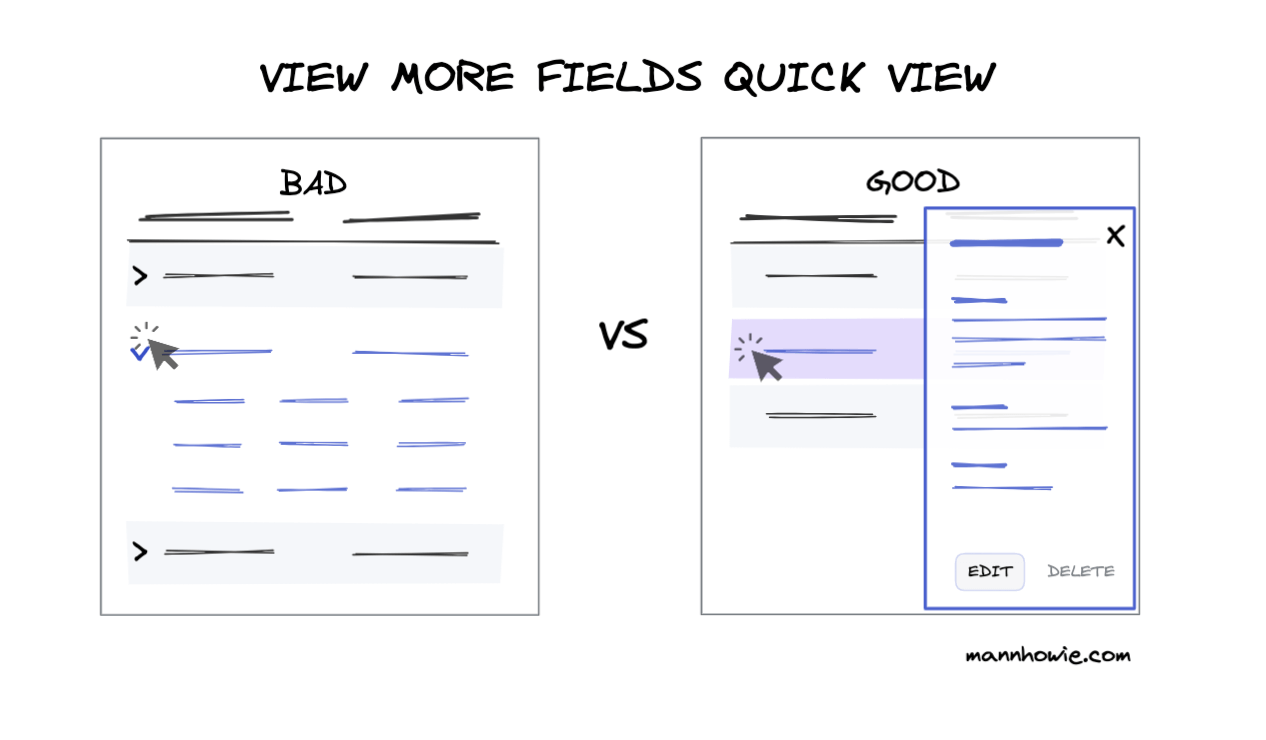
4. View more fields using quick view
Show more fields and controls of a single record by using a quick view (side-panel or modal). Place your edit and delete controls inside the quick view. Avoid collapsible accordions. They are inconsistent with table headers and cause user cleanup issues.
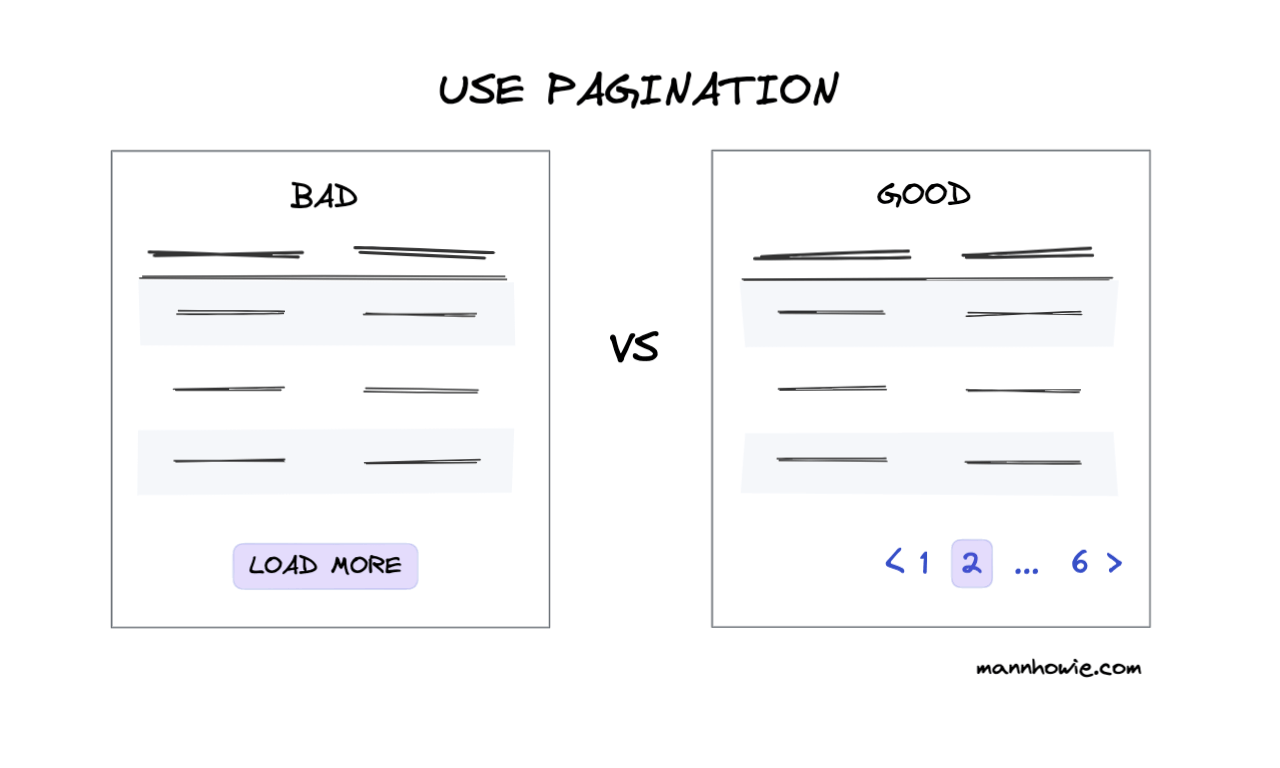
5. Use pagination for more records
Decide on the max rows each user should see then add pagination to indicate how many more records remain. Avoid “load more” buttons and infinite scroll. This causes issues of relocating records and false sense of completed search.
Conclusion
Data tables should help users find, compare and update data. Follow design patterns that help your users best achieve these goals.
Reference
Want more tips?
Get future posts with actionable tips in under 5 minutes and a bonus cheat sheet on '10 Biases Everyone Should Know'.
Your email stays private. No ads ever. Unsubscribe anytime.